Medical Genetics: Predictive Medicine

CURRENT APPLICATIONS
Predictive Medicine is currently being practiced today for a variety of preventive reasons, including the analysis of genetic information through advances of computer technology and assessing the diseases of individuals for all ages.
GENETIC TESTING
What is genetic testing?
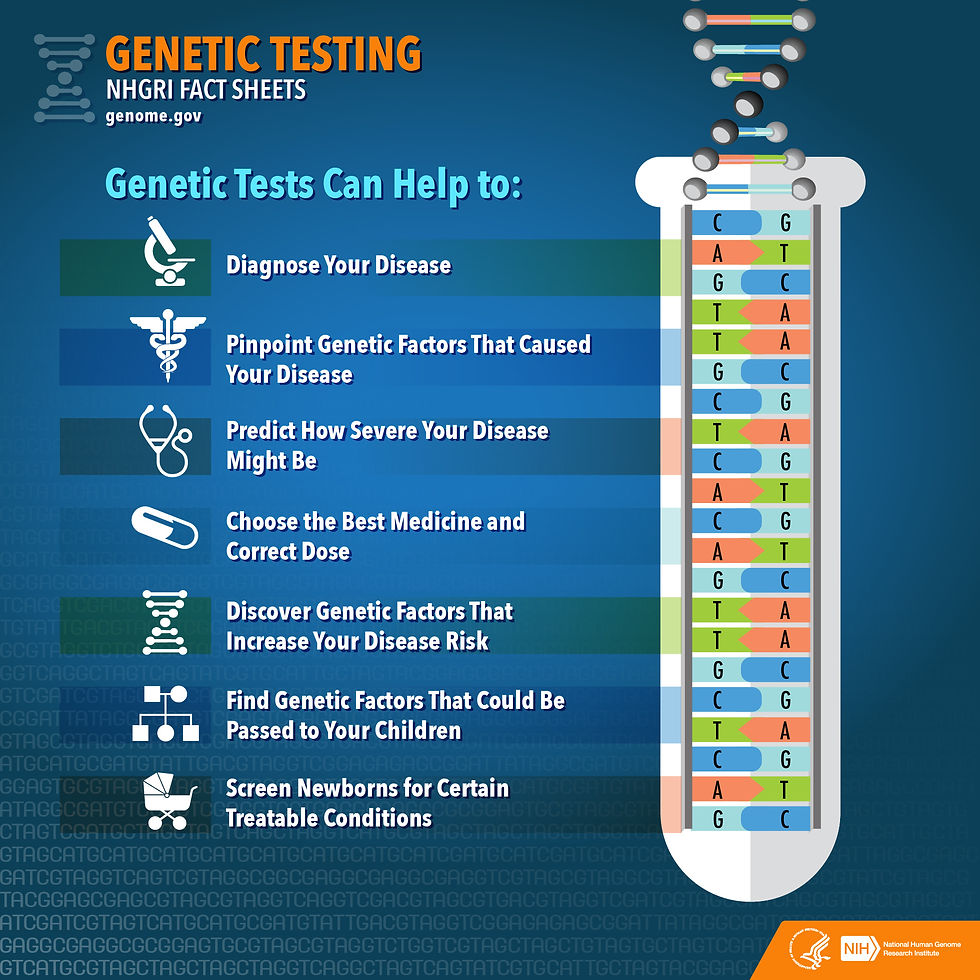
Genetic testing is the use of laboratory tests to determine the genetic status of an individual (5.2). Present applications of genetic testing in Predictive Medicine include (5.4):
-
diagnostic testing - used to isolate specific genetic or chromosomal conditions. This method confirms a diagnosis made according to physical signs and symptoms and can be performed at any time during one's life. Although it can identify specific genetic conditions, it is not yet available for all genes.
-
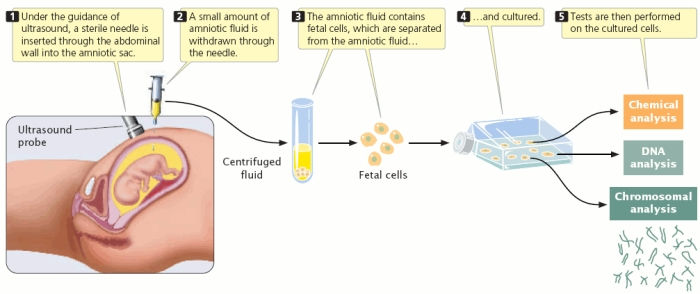
prenatal testing - can detect changes in a fetus's genes or chromosomes before birth occurs. This method can be done during pregnancy if there holds high risk that the baby may have a disorder. Performing prenatal testing helps conceiving couples with uncertainty and deciding on actions for a pregnancy.
-
carrier testing - capable of identifying people who carry a gene mutation copy that can cause a genetic disorder if the disorder is present in two copies. This method of testing is available to those who hold a history of a genetic disorder or an increased risk of genetic conditions.
-
preimplantation testing - Like prenatal testing, it is a specialized method of testing that can reduce the chances of having child with a particular genetic or chromosomal disorder. This test differs, however, because it is used to detect genetic changes in embryos created using assisted reproductive techniques like in vitro fertilization. In order to perform this test, a small number of cells are obtained from affected embryos and tested for their genetic changes. Embryos that are confirmed to have no changes are allowed to be implanted.
-
predictive risk testing - used to detect gene mutations that appear later in life. This test is helpful to indiviudals who do not hold features of a disorder during the time of testing because predictive risk testing is capable of identifying mutations that increase one's risk of inheriting a disorder through a genetic basis, like cancer. Ultimately, predictive risk resting can provide people with information about his or her risks of developing a disorder and can help him or her act upon the disease with medical attention.

(5a)
(5b)
(5e)

(5a)
GENETIC SCREENING
MEDICAL BIOINFORMATICS
What is genetic screening?
Genetic screening is the use of a set of diagnostic tests on a large number of individuals for the identification of people who are carriers of specific genetic disorders and those who are at high risk of having them. (5.2)
Newborn genetic screening is now being applied in order to test newly born babies for certain disorders and conditions that would complicate their normal development. This method of early detection and treatment prevents mental and physical disabilities that may threaten their lives. Newborn genetic screening often starts with a blood test that is taken 24 to 48 hours after the baby's birth. By law, all states in the U.S. must screen for at least 21 disorders and is encouraged and enforced by the Resources and Services Adminstration (HRSA). (5.3)
(5f)

What is medical bioinformatics?
Medical bioinformatics associates finding individual cell molecular parameters through the use of cytomics and single cell-bases microarrrays. By understanding a cell's restrictions and role in a disorder, predictive measures could be taken. This information is taken by computer-assisted identification and the characterization of few cell populations and desired gene clusters. Although this method is already active, researchers are still trying to find efficient ways to extract relevant predictive medicine parameters. (5.5)
(5g)